Next: 2 Technology Description Up: Appnotes Index Previous:Appnote RMI Index
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Next: 2 Technology Description
Up: Appnotes Index
Previous:Appnote RMI Index
By making use of robust, widely-accepted standards such as EDIF 4 0
0[Lau96] and STEP AP210[ISO96], the RASSP-MI ensures that the requirements
of predictability, completeness, consistency, and semantic correctness
in the exchange of product data are met. In addition, the standards-based
approach has made it possible to simultaneously utilize information from
a variety of domains, enabling advanced producibility analyses that could
not be performed previously.
The Manufacturing Resource Editor (MRE) is used by manufacturing engineers
to capture the structure, characteristics, and limitations of a manufacturing
facility in knowledge-base form. This information, combined with the intelligent
product data acquired from the PCA designer, make the advanced producibility
analysis functions performed by the PA and REF possible. The Rule Definition
Facility (RDF) provides a framework within which a manufacturing engineer
can capture process knowledge in the form of rules. This knowledge capture
tool is designed such that computer programming skills are not required
to operate it effectively, thereby making the tool accessible to a broad
spectrum of manufacturing engineers, not just those with a background in
computer science. The process knowledge captured with the RDF is used by
the REF, which executes it much like a program on product and process data.
Finally, the RASSP-MI provides support for Mitron's CIMBridge manufacturing
support software, which provides a variety of functions such as process
planning and Numeric Control (NC) program generation. It also includes
the Producibility Analyzer, which was commercialized by Mitron during the
course of the RASSP program.
This Application Note presents further information on the operational
details and benefits of the RASSP-MI components just introduced. In addition,
the results achieved by an implementation of the RASSP-MI in a production
environment are presented. Section 2 presents detailed operational characteristics
of the various components that make up the RASSP-MI. Section 3 presents
usage scenarios that illustrate how to effectively use the RASSP-MI to
support common activities. Section 4 presents results achieved by a Lockheed
Martin manufacturing facility using the RASSP-MI. Section 5 concludes with
a summary.
1.0 Introduction
The RASSP Manufacturing Interface (RASSP-MI), developed by SCRA's Advanced
Technology Institute and Lockheed Martin's Advanced Technology Labs (LMC-ATL),
enables significant reductions in the time and cost required to develop
and manufacture electronic systems while yielding improvements in product
quality. This is achieved by providing novel enterprise integration and
collaboration capabilities that enable distributed, multidisciplinary concurrent
engineering teams to work together effectively within a virtual enterprise.
Figure 1-1 illustrates this concept.
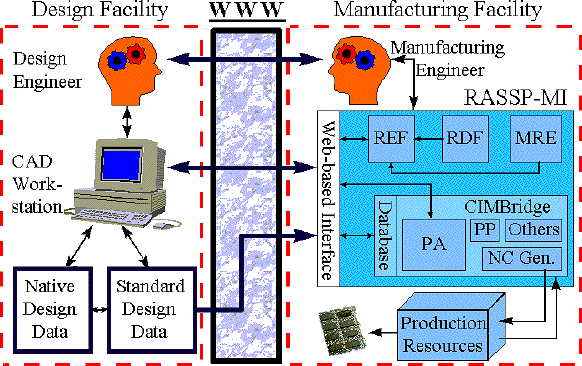
The RASSP-MI is composed of several elements that implement the overall
capability described. A World Wide Web (WWW) based interface provides users
external to the manufacturing facility hosting the RASSP-MI with easy to
use, robust access to the capabilities of the RASSP-MI. An external user
will typically be a Printed Circuit Assembly (PCA) designer interested in examining the producibility
characteristics of a PCA design early in the physical layout life-cycle design
stage. The designer can easily and securely transmit a PCA design to the
RASSP-MI, then use the Producibility Analyzer (PA) and the Rule Execution
Facility (REF) to determine how compatible the PCA design is with the hosting
manufacturing facility. Thus, the PCA designer can quickly and easily identify
manufacturing facility-specific producibility issues with a design once
preliminary component layout has occurred. By continuing to examine a design's
producibility and make corrections as necessary as it matures towards completion,
it is possible to eliminate all producibility issues before the design
is passed on to production, and thereby achieve first-pass production success.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Next: 2 Technology Description
Up: Appnotes Index
Previous:Appnote RMI Index